WELL Tip: What is the difference between the WELL v2 pilot and WELL v2?
To help you evaluate both versions and determine key similarities and differences, our team has compared the WELL v2 pilot and WELL v2 in three core areas.
Are you working on a WELL v2 pilot project and wondering how your team can best utilize the graduated version WELL v2? Eager to enroll your project but would like to understand the difference between the WELL v2 pilot and WELL v2?
To help you evaluate both versions and determine key similarities and differences, our team has compared the WELL v2 pilot and WELL v2 in three core areas:
- Rules: Insights on some of the programmatic changes in WELL v2
- Concepts: General overview of changes in each concept
- Features: Guidance on the WELL v2 Skybridge tool and other useful resources to use during your review
How do the rules for WELL v2 pilot compare to WELL v2?
Certification levels:
- Projects pursuing WELL Certification under WELL v2 can achieve one of four levels: Bronze, Silver, Gold and Platinum. For added flexibility, WELL v2 projects – both WELL Core and owner occupied – now have the option to pursue WELL Bronze.
- WELL Bronze Certification was previously only available to WELL v2 pilot projects pursuing WELL Core Certification.
- The minimum number of points per concept varies by certification level for owner-occupied projects in WELL v2 and differs from the WELL v2 pilot.
- WELL v2 and WELL v2 pilot projects are required to meet all preconditions and can pursue up to a maximum of 12 points per concept and 100 points across the 10 WELL concepts.
The table below summarizes the certification levels and points available for WELL v2:

Scoring:
- In WELL v2, the total points available for a feature is equivalent to the sum of its parts.
- In the WELL v2 pilot, each feature has a maximum point cap and in some cases the total sum of parts exceeds the feature cap. These point caps are not included in WELL v2 to streamline scoring.
Pathways:
- Multifamily residential projects (MFR):
- In WELL v2, MFR projects must utilize the WELL Certification pathway instead of WELL Core. In the pilot, MFR projects would select WELL Certification or WELL Core Certification, depending on their circumstances.
- Performance testing in dwelling units for precondition features is not required for MFR projects seeking certification at the Bronze or Silver level. For projects pursuing Gold or Platinum levels, testing is required in a sample of dwelling units. See features A01, W01, W02, L02 and T01 and the Sampling Rates for MFR section of the WELL Performance Verification Guidebook for more details. For optimizations, testing within dwelling units is required, regardless of the target level of certification.
- At recertification, for all levels of certification, testing is not required within dwelling units – only in common areas and spaces dedicated to building management.
- In WELL v2, MFR projects must utilize the WELL Certification pathway instead of WELL Core. In the pilot, MFR projects would select WELL Certification or WELL Core Certification, depending on their circumstances.
How do the concepts compare between the WELL v2 pilot and WELL v2?
WELL v2 comprises 108 features (not including beta features) – 24 preconditions and 84 optimizations – within the same 10 concepts you are familiar with from the WELL v2 pilot: Air, Water, Nourishment, Light, Movement, Thermal Comfort, Sound, Materials, Mind, and Community. WELL v2 also continues to reward creativity from projects through the 5 Innovation features.

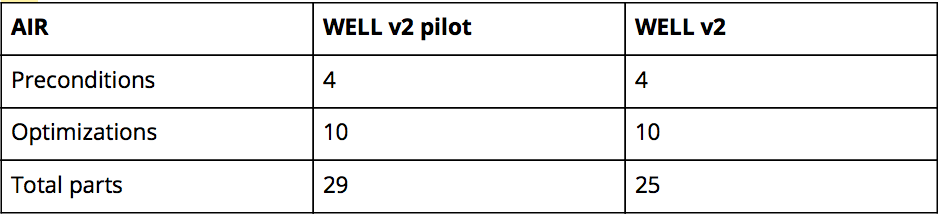
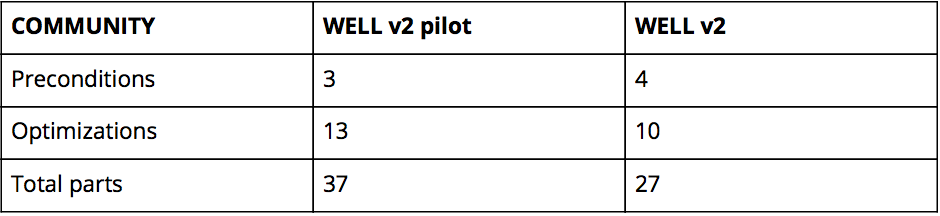
Below, each of the 10 concepts are broken down by key changes that were made from the WELL v2 pilot, including a table that summarizes the comparison between preconditions, optimizations, total parts and total points available between the two rating systems.
Note: Unless otherwise stated, the features below refer to WELL v2 features.
Air
AIR
- In order to remain current with updated research and best practices and to match pollutants tested with those commonly found in buildings, the list of required thresholds for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) were adjusted in Feature A01: Air Quality and Feature A05: Enhanced Air Quality. This led to an overall reduction in the number of species (types) of VOCs requiring on-site performance testing for the A01, and introduced testing requirements for several additional species in A05.
- Feature A09: Pollution Infiltration Management is now split into two parts to reward projects for these two different strategies: one to address the design of healthy entryways and the second to address envelope commissioning.
- Feature A13: Enhanced Air Supply provides projects with the option to achieve the feature through the provision of 100% outdoor air, in addition to the existing option of using activated carbon filters on partially recirculated air. Furthermore, in response to feedback from the Task Force on COVID-19 and Other Respiratory Infections, recirculated air must also be treated with UVGI or media filters to combat airborne infectious diseases.
- Feature A14: Microbe and Mold Control focuses on the implications of mold and bacteria growth with the building mechanical system. Minimizing unintentional moisture, more generally, is addressed in Feature W07: Moisture Management.
Water
WATER

- Feature W02: Drinking Water Quality contains two parts from what was seven parts in the corresponding WELL v2 pilot Feature W02: Water Contaminants. Part 2 offers flexibility for projects to meet the requirements through provision of a municipal water quality report or on-site testing conducted by a professional. This reduces the number of samples required and allows for a greater focus on those parameters most meaningful to test due to their likelihood of varying across different sampling points (e.g., faucets) within a building.
- In WELL v2, all requirements related to monitoring, previously spread across pilot preconditions, have been consolidated into Part 1 of Feature W03: Basic Water Management. Part 1 simplifies annual reporting by requiring basic parameters to be sampled annually. In addition, only those parameters outlined in Feature W02 Part 1 which are on the cusp or at the threshold, are to be documented in annual reporting.
- Feature W03: Basic Water Management retains the requirement on creating a Legionella management plan but provides more detailed information on plan requirements and what may be appropriate for a particular project type (e.g., an interiors project vs. a building that the project owns and occupies).
- Feature W05: Drinking Water Quality Management focuses on the testing, monitoring and maintaining of water for quality. This differs from the related WELL v2 pilot Feature W05, which placed greater emphasis on implementing specific water treatment strategies. This change values a risk assessment approach while still preserving the transparency in providing testing results to users of the space that was part of the WELL v2 pilot Feature W05.
- Feature W08: Hygiene Support expands beyond handwashing to include the accessibility requirements found in the WELL v2 pilot Community Feature C14: Bathroom Accommodations. Feature W08 serves as a strategy both for providing bathrooms that accommodate users with diverse needs and improving hygiene.
Nourishment
NOURISHMENT

- In WELL v2, overarching changes were introduced to clarify the scope and applicability of WELL features, including:
- The addition of a new space type -“Dining Spaces” - is specific to on-site food preparation and/or full-service dining. These projects include a commercial kitchen and food service staff. Foods prepared on-site include foods assembled on-site and foods prepared for immediate consumption. Projects without these facilities are not eligible to pursue these features.
- For example, Feature N01: Fruits and Vegetables now includes specific requirements for Dining Spaces, which offers a pathway for projects such as restaurants and food retailers to encourage fruit and vegetable consumption.
- Added language clarifies the scope of Nourishment features. Features may reference “…all foods and beverages sold or provided on a daily basis by (or under contract with) the project owner…” to spell out how the requirements apply to food and beverage offerings.
- More information on these specific changes is available in the Overview section of WELL v2.
- The addition of a new space type -“Dining Spaces” - is specific to on-site food preparation and/or full-service dining. These projects include a commercial kitchen and food service staff. Foods prepared on-site include foods assembled on-site and foods prepared for immediate consumption. Projects without these facilities are not eligible to pursue these features.
- Feature N02: Nutritional Transparency addresses food allergens through signage and the provision of food allergen training for food service staff. This change is in place of food allergen labeling, which was a part of the related WELL v2 pilot Feature N02: Nutritional Transparency. In WELL v2, food allergen labeling is addressed in Feature N09: Special Diets.
- Feature N07: Nutrition Education houses all requirements related to education within the Nourishment concept, including gardening or planting workshops, which were previously a requirement in WELL v2 pilot Feature N12: Food Production.
- The educational requirements in this feature, and across all features with educational requirements in the standard, now focuses solely on education provided through workshops or trainings rather than passive education such as books or pamphlets. This shift allows the users to more effectively engage with the health topic.
Light
LIGHT

- Feature L01: Light Exposure specifies multiple options for projects to meet the requirements for indoor light exposure, similar to the WELL v2 pilot Feature L01: Light Exposure and Education. L01 no longer contains requirements for visible light transmittance of glazing, and these requirements are now solely addressed in Feature L05: Daylight Design Strategies.
- Feature L02: Visual Lighting Design has two pathways for projects to choose from when ensuring the provision of appropriate illuminances on work planes. The first pathway is retained from the WELL v2 pilot Feature L02: Visual Lighting Design, allowing projects to choose the lighting requirements based on selected lighting reference guidelines. A new pathway allows projects to meet predetermined light levels verified through on-site performance testing. This option provides flexibility to all projects and may be especially useful to existing buildings or projects with little variation in space type.
- Feature L04: Electric Light Glare Control is streamlined to address electric light glare. The components of solar glare, previously in the related WELL v2 pilot Feature L04: Glare Control, have moved to WELL v2 Feature L05: Daylight Design Strategies. L04 now also provides an option for industrial spaces to meet the intent by minimizing glare caused by electric light.
- Encouraging creativity from project teams is built into an option in Feature L07: Visual Balance. Projects have the option to either meet preset parameters or work with a lighting professional to design lighting for visual balance that takes into account several considerations without prescribing exact parameters. For both options, project teams can describe how their lighting strategy meets the feature requirements through a professional narrative.
- The requirements for Feature L09: Occupant Lighting Control have been revised from the related WELL v2 pilot requirements in Feature L08: Occupant Control of Lighting Environments to provide project teams with additional guidance on ambient lighting control and personal lighting control.
Movement
MOVEMENT

- Feature V02: Ergonomic Workstation Design is similar to the WELL v2 pilot Feature V02: Visual and Physical Ergonomics. Part 5 focuses on orienting employees to their workstation and removes passive education strategies.
- Feature V03: Circulation Network centers around aesthetic design of staircases, point-of-decision signage and staircase location, no longer containing requirements for hallways. The applicability of this feature has also been clarified for interiors projects, with guidance found in the certification note section in each part on the digital standard.
- Feature V04: Facilities for Active Occupants includes requirements for an adequate cycling network to complement the bike parking requirements in order to support active commuting. Projects can demonstrate the presence of a cycling network through Bike Score®, the measured distance to an existing cycling network or document future plans for a cycling network.
- Feature V06: Physical Activity Opportunities offers projects tiered points, where more points are awarded for increasing the duration and frequency of physical activity programming available for students and/or employees. In WELL v2, the thresholds for points awarded to projects with employees and university students better aligns with physical activity guidelines.
Thermal Comfort
THERMAL COMFORT

- Feature T01: Thermal Performance offers increased flexibility for projects by outlining three options for projects to meet the feature intent: through on-site performance testing of thermal conditions, providing long-term thermal data or attesting that occupants find the environment to be thermally comfortable through a survey.
- Feature T04: Individual Thermal Control addresses thermal comfort through personal thermal comfort devices and a flexible dress code policy. The WELL v2 feature breaks out personal thermal comfort devices into two parts, covering cooling and heating options, which were previously a single part in the WELL v2 pilot feature T04.
- In Feature T07: Humidity Control, project teams have a variety of options to achieve the intent of maintaining the appropriate level of humidity, including a new option to provide long-term humidity data.
Sound
SOUND

- Feature S01: Sound Mapping has been revamped, such that the labeling of acoustical zones incorporates an element of planning in which project teams demonstrate how their projects are addressing sound transmission between adjacent loud and quiet zones. The requirements on managing background noise level and acoustical privacy are combined in a single part in WELL v2.
- Feature S02: Maximum Noise Levels has a tab for dwelling units to provide further clarity for this space type.
- Feature S03: Sound Barriers combines requirements for wall and door specifications into a single part. S03 also includes a performance-based option for background noise management or for wall insulation to accommodate a variety of project types, new construction and existing buildings alike.
- Feature S04: Reverberation Time includes two pathways for projects to achieve the feature, including a design-based option and a performance-based option.
- Feature S05: Sound Reducing Surfaces draws on parts 1 and 2 of the WELL v2 pilot Feature S04: Sound Absorption, covering the use of acoustic materials that absorb and/or block sound to support focus and reduce reverberation.
- Feature S06: Minimum Background Sound focuses on increasing acoustical privacy within and between occupied spaces. In the WELL v2 pilot, the related feature is S05: Sound Masking. Both cover the use of a dedicated sound masking system, but S06 requires that the requirements of Part 1 are verified through a commissioning report, whereas in the WELL v2 pilot Feature S05, the requirements of the feature are verified through performance testing.
Materials
MATERIALS

- The Materials concept underwent the most significant changes. These largely represent a fundamental restructuring to more clearly focus on the core narrative of the concept: remediation of legacy contaminants and restrictions in their use, selection of healthier products and provision of healthier building operations and maintenance.
- The features in the Materials concept saw a revamp around the reference material, no longer referring to US-based code and regulations, making the concept more globally applicable and minimizing the need for project teams to submit or use equivalencies.
- Another overarching change to Materials is around verification methods. Now, where Letters of Assurance are required for Materials features, project teams are also asked to submit specification sheets from the product manufacturer.
- Feature X02: Interior Hazardous Materials Management combines Feature X02: Hazardous Material Abatement and Feature X05: In-Place Management from the WELL v2 pilot.
- Feature X04: Site Remediation provides project teams the option to meet the requirements for the environmental site assessment through local applicable regulations.
- Feature X05: Enhanced Material Restrictions combines requirements from the WELL v2 pilot Feature X08: Hazardous Material Reduction and Feature X10: Volatile Compound Reduction. The requirements in Feature X05 are organized around product type rather than by chemical type. This feature also specifies requirements for electrical or electronic products.
- Feature X06: VOC Restrictions focuses on VOC content and pulls from the WELL v2 pilot Feature X11: Long-Term Emission Control and Feature X12: Short-Term Emission Control.
- Feature X07: Materials Transparency no longer contains requirements for a percent by cost of materials but rather organizes requirements around a total count of products.
- Feature X08: Materials Optimization pulls from the WELL v2 pilot Feature X13: Enhanced Material Precaution, and no longer requires percent by cost of products to comply with the feature language.
- Feature X09: Waste Management now spells out the requirements of a sufficient waste management plan, providing project teams with additional detail without referencing US regulations.
- Feature X10: Pest Management and Pesticide Use Use covers the requirements of the WELL v2 pilot Feature X07: Pesticide Use.
- Feature X11: Cleaning Products and Protocols includes additional detail that project teams must specify in regards to cleaning practices, including the training done to protect cleaning staff who perform the necessary cleaning.
Mind
MIND

- The Mind concept includes changes in the overall feature structure to better center around key strategies related to mental health.
- Feature M02: Nature and Place houses the requirements on beauty and design from the Feature C02: Integrative Design Part 2 in the WELL v2 pilot.
- Projects have the option to provide the education offered through Feature M04: Mental Health Education and Feature M11: Substance Use Services either in-person or virtually.
- In response to feedback from the Task Force on COVID-19, this change was made throughout the standard.
- Feature M06: Restorative Opportunities contains two parts and incorporates aspects of Feature M11: Sleep Support from the WELL v2 pilot.
- Feature M09: Enhanced Access to Nature is broken down into two separate parts to address indoor and outdoor access to nature. M09 also provides project teams with greater flexibility in documenting the quantity of biophilia needed to satisfy requirements.
Community
COMMUNITY
- The Community concept was streamlined to focus the scope around health equity and social inclusion as key impact areas.
- The Community concept addresses planning for emergency situations through a couple of avenues. The first is the inclusion of a new precondition, Feature C03: Emergency Preparedness. Previously, this was addressed through Part 1 of WELL v2 pilot Feature C15: Emergency Preparedness. Part 2 of the WELL v2 pilot Feature C15: Emergency Preparedness was retained as an optimization, Feature C14: Emergency Resources, in WELL v2. Feature C14 also covers the provision of opioid response kits and training that was previously covered in the WELL v2 pilot Feature M15: Opioid Emergency Response Plan.
- Feature C06: Health Services and Benefits houses what is Feature C07: Community Immunity in the WELL v2 pilot. Additionally, Feature C06 requires coverage of infectious disease testing in the health benefits plan. Finally, Feature C06 includes a part centered around the provision of sick leave, which was not previously addressed in the WELL v2 pilot.
- Feature C07: Enhanced Health and Wellness Promotion covers the educational component of the WELL v2 pilot Feature C01: Health and Wellness Awareness. Education strategies required in C07 focus on interactive forms including workshops and seminars.
- To advance leadership, Feature C08: New Parent Support now addresses non-primary caregiver leave and allows projects to select from three options for added flexibility.
- Feature C12: Diversity and Inclusion, related to the WELL v2 pilot Feature C12: Organizational Transparency, has been expanded to focus on diversity and inclusion more specifically through the addition of requirements around creating a comprehensive, custom internal program related to diversity and inclusion.
Innovation
INNOVATION

- Through Feature I01: Innovate WELL, projects can now exceed the 12-point maximum per concept as outlined in the Overview instead of AAP #00010 in the WELL v2 pilot. Submissions are worth one point per part, regardless of the listed point value of that part.
- Feature I01: Innovate WELL focuses solely on proposals for innovative strategies that are not already covered in other WELL v2 features. This differs from Feature I01: Innovate WELL in the WELL v2 pilot in which projects could propose strategies that go above and beyond the existing requirements for the WELL v2 pilot features. WELL v2 projects that wish to take their efforts to the next level will now find these opportunities embedded directly in feature language and will be rewarded through tiered points.
- In order to encourage greater accessibility to tours of WELL Certified spaces, Feature I03: Experience WELL Certification requires projects to open these free tours up to the public, thus facilitating more opportunities to experience and learn about WELL Certification.
What is the WELL v2 Skybridge tool?
Use the WELL v2 Skybridge tool along with these other useful resources during your review for WELL Certification.
How do I upgrade my project from WELL v2 pilot to WELL v2?
IWBI has created the WELL v2 Skybridge tool, a compilation of the approved equivalent feature language between the WELL v2 pilot and WELL v2.
How do I use the WELL v2 Skybridge tool?
The WELL v2 Skybridge tool outlines approved feature language substitutions between the WELL v2 pilot and WELL v2. There are several ways that project teams can leverage this tool. For project teams that are pursuing the WELL v2 pilot, this tool covers WELL v2 features that can be substituted for WELL v2 pilot features. For project teams that may have started their journey in pursuit of the WELL v2 pilot but are interested in upgrading to WELL v2, this tool covers WELL v2 pilot features that can be substituted for WELL v2 features.
Where can I find this tool and any additional support?
The WELL v2 Skybridge tool is available for download here. The Overview section of WELL v2 is a great resource for learning about how to apply WELL v2 in practice. If technical questions arise when reviewing WELL v2, our customer service team is ready and eager to support — just reach out using the form on the Contact Us page. For registered projects, WELL coaching support is available if you have any additional questions about WELL v2 or upgrading your project to the latest version. Reach out via the support tab of your WELL digital platform account.







